7 Female Reproductive System
Topic: Female Reproductive System
Text Reference: Chapter 7. Female Reproductive System
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the female reproductive system
Prefixes
a- (absence of, without)
an- (absence of, without)
dys- (painful, difficult, abnormal, labored)
endo- (within)
peri- (surrounding)
Combining Forms
arche/o (first, beginning)
cervic/o (cervix)
colp/o (vagina)
endometri/o (endometrium)
episi/o (vulva)
gyn/o (woman)
gynec/o (woman)
hymen/o (hymen)
hyster/o (uterus)
mamm/o (breast)
mast/o (breast)
men/o (menstruation)
metr/i (uterus)
metr/o (uterus)
oophor/o (ovary)
pelv/i (pelvis, pelvic bones, pelvic cavity)
perine/o (perineum)
salping/o (uterine tube, fallopian tube)
trachel/o (cervix)
vagin/o (vagina)
vulv/o (vulva)
Suffixes
-al (pertaining to)
-atresia (occlusion, closure)
-clesis (surgical closure)
-ectomy (excision, surgical removal)
-gram (the record, radiographic image)
-graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
-itis (inflammation)
-logist (specialist or physician who studies and treats)
-logy (study of)
-osis (abnormal condition)
-pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
-plasty (surgical repair)
-rrhaphy (suturing, repairing)
-rrhea (flow, discharge)
-salpinx (uterine tube)
-scope (instrument used for visual examination)
-scopy (visually examining)
-tomy (cut into, incision)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following terms.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
Practice pronouncing and defining these medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
adenomyosis (ad-ĕ-nō-mī-Ō-sis)
anovulation (an-ov-yŭ-LĀ-shŏn)
Bartholin’s glands (BAR-tō-lĭns glăns)
breast cancer (brest KAN-sĕr)
cervical cancer (SĔR-vi-kăl KAN-sĕr)
contraception (kon-tră-SEP-shŏn)
dyspareunia (dis-pă-ROO-nē-ă)
endometrial cancer (en-dō-MĒ-trē-ăl KAN-sĕr)
fibrocystic breast changes (FCC) (fī-brō-SĬS-tĭk brest)
fistula (FIS-chŭ-lă)
hormonal replacement therapy (HRT)
menopause (MEN-ŏ-poz)
oligoovulation (ol-i-gō-ov-yŭ-LĀ-shŏn)
ovarian cancer (ō-VAR-ē-ăn KAN-sĕr)
ovulation (ov-yŭ-LĀ-shŏn)
papanicolaou Smear (păp-ă-NĒ-kă-low smēr)
pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) (pŏl-ē-SĬS-tĭk Ō-vă-rē SĬN-drōm)
premenstrual syndrome (prē-MĔN-stroo-ăl SĬN-drōm)
prolapse (PRŌ-laps)
speculum (SPEK-yŭ-lŭm)
toxic shock syndrome
tubal ligation (TOO-băl lī-GĀ-shŏn)
uterine fibroid (ŪT-ĕ-rīn FIB-royd)
uterine prolapse (ŪT-ĕ-rīn PRŌ-laps)
vaginal fistula (VAJ-ĭn-ăl FIS-chŭ-lă)
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated terms.
Female Reproductive System Term Abbreviations
BC (birth control)
Cx (cervix)
D&C (dilation and curettage)
FCC (fibrocystic breast changes)
GYN (gynecology)
HPV (human papillomavirus)
HRT (hormone replacement therapy)
HSG (hysterosalpingogram)
IUD (intrauterine device)
LAVH (laparoscopically assisted vaginal hysterectomy)
PCOS (polycystic ovarian syndrome)
PID (pelvic inflammatory disease)
PMS (premenstrual syndrome)
SHG (sonohysterography)
TAH/BSO (total abdominal hysterectomy/bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy)
TLH (total laparoscopic hysterectomy)
TSS (toxic shock syndrome)
TVH (total vagianal hysterectomy)
TVS (transvaginal sonography)
UAE (uterine artery embolization)
Reproductive Sexually Transmitted Infections (STI) Abbreviations
AB (Antibiotic)
CT (Chlamydia)
GC (Gonorrhea)
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus)
PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
STD (Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
STI (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories.
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Use terms related to the female reproductive system.
Label the following female reproductive system anatomy.
cervix | endometrium | fimbriae | fundus | myometrium | ovary | perimetrium | uterine tube | vagina
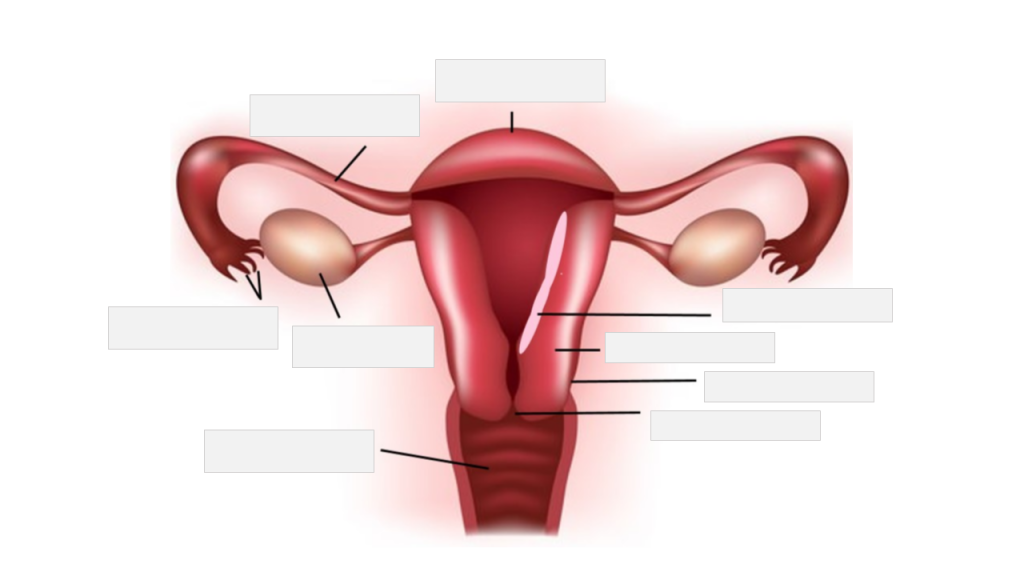
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
cysts | dysmenorrhea | endometrial | endometriosis | laparoscopy | pain | pelvis | tissue | transvaginal
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM – MEDICAL REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Stacey ROBERTS
AGE: 28 Sex: Female
DOB: October 27
DATE OF ASSESSMENT: July 22
ADMITTING PHYSICIAN: Adam Vance, MD, Gynecology
DIAGNOSIS: Endometriosis
HISTORY: This 28-year-old white female came to me with symptoms of ________. She presented with ________, menorrhagia, and pain with intercourse.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: During a ________ exam, abnormalities were felt. A ________ ultrasound was performed, and ________ were identified.
TREATMENT: I have discussed the results of the ultrasound and have recommended a laparoscopy to provide more information on the location, extent, and size of the ________ implants. A ________ sample will be sent for further testing. If possible, the endometriosis implants will be removed.
PLAN: Ms. Roberts has agreed to the laparoscopy. I have prescribed Orilissa to help with the ________. My office will set up an appointment for the ________.
___________________________
Adam Vance, MD, Gynecology
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
abdominal | auscultation | Blood pressure | chronic | edema | menorrhagia | murmur | oophoritis | ovarian | RLQ | spotting | urination
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM – MEDICAL REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Megan WESTOVER
AGE: 29
SEX: Female
DOB: November 22
DATE OF ASSESSMENT: June 4
ATTENDING PHYSICIAN: Adam Vance, MD, Gynecology
HISTORY: A 29-year-old woman complains of right ________ pain. She has fever with chills, nausea, and pain during ________ for 3 days. She is in the 4th day of her menstrual cycle and has ________. She has had intermenstrual ________ for the last 3 menstrual cycles. She had a hysterectomy due to a breast cancer 9 years ago. She has no other history of ________ illness.
PHYSICAL AND EXAMINATION: VITAL SIGNS: Temperature 102.2, ________ 115/75, and pulse 92, regular. Respiratory rate 16. LUNGS: Normal breath sounds. HEART: No ________, regular rhythm. ABDOMEN: There is a tenderness to deep palpation in the ________. Pain triggers when the patient bends forward. Normal to ________. BACK: No flank tenderness. EXTREMITIES: Normal with no ________.
LABORATORY: No UTI, urinalysis done in the clinic negative.
ASSESSMENT: Rule out ________. No evidence of UTI currently.
PLAN
- CBC lab testing.
- Pelvic ultrasound focused on ________ structures, transvaginal ultrasound.
- Begin treatment empirically with Ampicillin 500 mg daily.
- Follow up with the patient after the blood and ultrasound results.
___________________________________
Adam Vance, MD, Gynecology
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
breast | chemotherapy | cyanosis | distended | erythema | HEENT | lesion | mastectomy | murmurs | Weight |
FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Abigail LANGMAN
AGE: 51
SEX: Female
DOB: July 27
DATE OF CONSULTATION: October 8
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Adam Vance, MD, OB/GYN
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Possible breast cancer.
HISTORY: Patient is a 51-year-old woman here for a check-up because of a suspicious lump that was found on her yearly mammogram. Patient is worried about possible ________ cancer.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: GENERAL: No acute distress. VITAL SIGNS: Temperature is 98.1°F. Pulse is 72, BP is 110/72 mm Hg. Respirations 16. ________ is 186 pounds, height is 5 feet, 8 inches. ________: Eyes are equal and responsive. Ears are normal, no discharge. Nose is normal. Throat is normal and without ________. LUNGS: Clear to auscultation. CARDIOVASCULAR: Regular rate and rhythm, no ________. ABDOMEN: Palpation is soft, not ________, nontender. BREAST: RIGHT: Tender to the touch on right side and has a hard lump about the size of a golf ball near the axilla. LEFT: Normal to the touch, no discomfort. EXTREMITIES: Without edema, ________, or clubbing.
SOCIAL HISTORY: Mother had breast cancer at the age of 48 and had a ________ to remove the left breast. Patient has been scheduled for yearly mammograms since the age of 45 to check for possible signs of early breast cancer. Father has a history of stage 1 rectal cancer treated with 3 rounds of ________. The patient does not smoke or use recreational drugs, she does like a glass of wine 3-4 nights a week.
Patient states she is quite worried since scheduling an appointment to follow up her mammogram results. Patient has experiencing anxiety which is affecting her eating and sleeping routine.
ASSESSMENT: Patient is a 51-year-old woman here for a check-up because a suspicious lump found on her yearly mammogram. Patient is otherwise healthy and is not currently on any medications.
PLAN
- Ultrasound of the right breast.
- Biopsy of the ________ for pathology. Avoid overexertion or lifting of arms above shoulder height after the biopsy
- Follow-up appointment in 2-3 weeks for results.
________________________
Adam Vance, MD, OB/GYN
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
The site of implantation for a fertilized egg or the layer that sheds during menstruation if no egg is fertilized is called…
- endometrium
- oocyte
- puerperium
Hysterectomy is the…
- surgical removal of the uterus
- surgical removal of the fallopian/uterine tubes
- surgical removal of the breast(s)
Painful periods is called…
- Dysmenorrhea
- Oligomenorrhea
- Amenorrhea
Painful intercourse is called…
- dysuria
- dysmenorrhea
- dyspareunia
The superior portion of the vagina is called…
- fornix
- axilla
- Bartholin’s glands

