5 Urinary System
Topic: Urinary System
Text Reference: Chapter 5. Urinary System
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the urinary system
Prefixes
a- (absence of, without)
an- (absence of, without)
dia- (through, complete)
dys- (painful, abnormal, difficult, labored)
poly- (many, much)
Combining Forms
albumin/o (albumin)
azot/o (urea, nitrogen)
blast/o (developing cell, germ cell)
cyst/o (bladder, sac)
glomerul/o (glomerulus)
glyc/o (sugar)
glycos/o (sugar)
hydr/o (water)
lith/o (stone, calculus)
meat/o (meatus)
nephr/o (kidney)
noct/i (night)
olig/o (few, scanty)
pyel/o (renal pelvis)
py/o (pus)
ren/o (kidney)
ureter/o (ureter)
urethr/o (urethra)
urin/o (urine, urinary tract)
ur/o (urine, urinary tract)
vesic/o (bladder, sac)
Suffixes
-al (pertaining to)
-ary (pertaining to)
-cele (hernia, protrusion)
-emia (in the blood)
-gram (the recorded radiographic image)
-graph (instrument used to record)
-graphy (process of recording, radiographic imaging)
-iasis (condition)
-esis (condition)
-itis (inflammation)
-lith (stone)
-lysis (loosening, dissolution, separating)
-megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
-oma (tumour, swelling)
-osis (abnormal condition)
-pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
-ptosis (drooping, sagging, prolapse)
-rrhaphy (suturing, repairing)
-scope (instrument used for visual examination)
-scopic (pertaining to visual examination)
-scopy (visual examination)
-stomy (creation of an artificial opening)
-tomy (cut into, incision)
-tripsy (surgical crushing)
-uria (urine, urination)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following terms.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
Practice pronouncing and defining these medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
deamination (dē-am-ĭ-NĀ-shŏn)
distended (dis-TEN-ded)
enuresis (en-ū-RĒ-sĭs)
hemodialysis (HD) (hē-mō-dī-ĂL-ĭ-sĭs)
hydrostatic (hī-drō-STAT-ik)
incontinence (in-KONT-ĭn-ĕns)
micturate (MĬK-tū-rāt)
sphincter (SFĬNK-tĕr)
stricture (STRIK-chŭr)
urinal (Ū-rĭn-ăl)
void (VOYD)
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated terms.
ARF (acute renal failure)
BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
cath (catheter, catheterization)
CKD (chronic kidney disease)
ESRD (end-stage renal disease)
ESWL (extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy)
HD (hemodialysis)
KUB xray (kidney, ureter, and bladder xray)
OAB (overactive bladder)
SG (specific gravity)
UA (urinalysis)
UTI (urinary tract infection)
VCUG (voiding cystourethrogram)
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories.
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Use terms related to the urinary system.
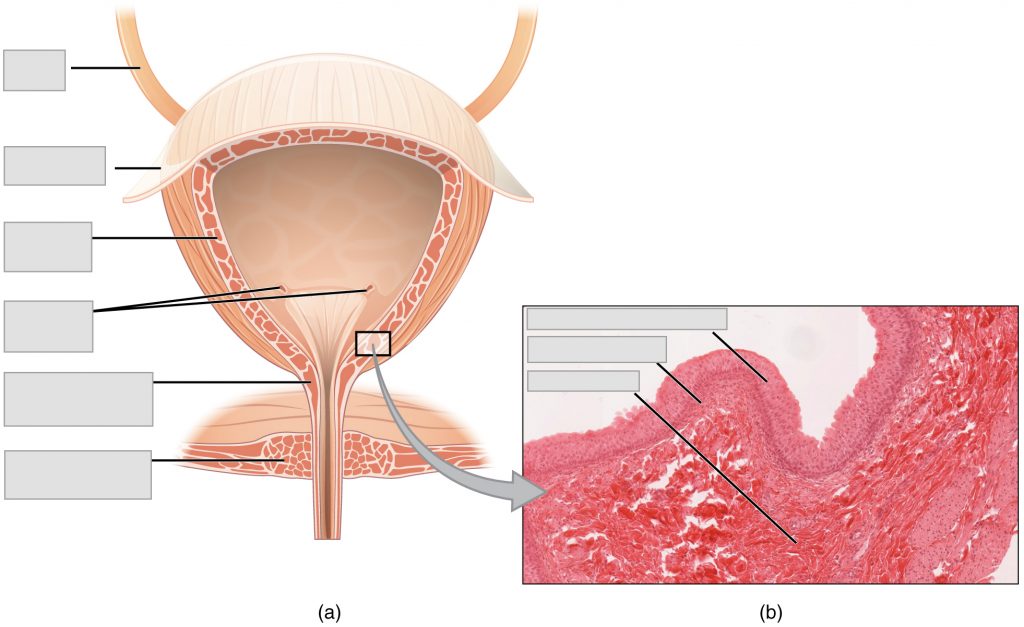
Label the following urinary system bladder anatomy.
detrusor muscle | external urethral sphincter | internal urethral sphincter | lamina propria | peritoneum | submucosa | transitional epithelium | ureter | ureteral openings
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
bladder | draped | fragmented | lumen | prepped | proximal | recovery | ureteral
URINARY SYSTEM – OPERATIVE REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Cindy WARD
AGE: 48
DOB: September 19
SEX: Female
DATE OF SURGERY: January 8
SURGEON: Steve Foster, MD, Urologist
ASSISTANT: Michelle Stevenson, MD
ANESTHESIOLOGIST: Ryan Haywood, MD
ANESTHESIA: General
PREOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Left proximal ureteral stones.
POSTOPERATIVE DIAGNOSIS: Left proximal ureteral calculi.
INDICATIONS: The patient is a 48-year-old female with a history of kidney stone disease, who has severe left flank pain and was found to have an obstructing large left proximal ________ stone.
OPERATIVE PROCEDURE: After induction of general anesthesia, the patient was placed in the lithotomy position. Patient was ________ and ________ in the usual sterile fashion. A #19-French cystoscope was inserted under camera vision. The urethra was unremarkable. The scope was passed into the bladder. The ________ mucosa was normal throughout. Under fluoroscopic control, a guidewire was placed up the left ureter and bypassed the stone. This was difficult at first, but the guidewire was eventually manipulated around the stone into the ________ collecting system. A rigid ureteroscope was then negotiated up the left ureter alongside the guidewire up to the stone, which was at the junction.
The stone was quite large and occupied the entire ________ of the ureter. Lithotripsy was then performed under camera vision. Using the Holmium laser, the stone was ________ into multiple fragments, all of which were then individually basketed. Some of the stones were sent for analysis. Further ureteroscopy up to the kidney failed to reveal any significant sized fragments. Therefore, the ureteroscope was removed.
The procedure was tolerated by the patient without complications. The patient was taken to the ________ room in stable condition.
________________________
Steve Foster, MD, Urologist
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
dysuria | foul | leukorrhea | nausea | pain | shortness | Urinalysis | urine | UTIs
URINARY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Renee WOODS
AGE: 32
SEX: Female
DOB: June 17
DATE OF CONSULTATION: January 8
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Steve Foster, MD, Urology
REASON FOR CONSULTATION: Urinary Tract Infection.
HISTORY: The patient is a 32-year-old female who is complaining of pain on urinating. Patient states it began approximately 3 days ago. The patient describes symptoms of ________ and increased frequency to the washroom. Patient states they usually go to the washroom to urinate 4-5 times a day, but starting 3 days ago, she started going 10-12 times per day. Sometimes no ________ comes out. The urine has a ________ odor and is cloudy. States there has been lower abdomen ________ since yesterday, and says it is worse when she tries to go with no result. Patient has had the same sexual partner for 10 years. She has a history of ________ and feels this is the same.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: GENERAL: No weakness, or tiredness. VITALS: Blood pressure 120/80, heart rate 70 and respirations 16. Patient weighs 150 pounds. LUNGS: No cough or ________ of breath. GASTRO: Denies ________, vomiting or change in bowel habits.
URINARY/REPRODUCTIVE: Denies hematuria, or any ________.
ASSESSMENT: Did a urinalysis on patient. ________ revealed leukocytes 3+.
PLAN
1. Treat with Ampicillin 400 mg q.i.d.
2. Return to office if no improvement within 48 hours.
______________________________
Steve Foster, MD, Urology
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
The removal of an amino group from a molecule…
- Deamination
- Calyces
- Voiding
A measure of how acidic or alkaline a substance is, as determined by the number of free hydrogen ions in the substance…
- pH
- Apical
- Osmosis
Relating to the equilibrium of liquids and the pressure exerted by liquid at rest…
- Solutes
- Hydrostatic
- Mitochondria
The outermost layer of the wall of a blood vessel…
- Hydrostatic
- Adventitial
- Pseudostratified
Any of a group of compounds with varying hormone-like effects…
- Solutes
- Prostaglandins
- Excretion

