6 Male Reproductive System
Topic: Male Reproductive System
Text Reference: Chapter 6. Male Reproductive System
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the male reproductive system
Prefixes
a- (absence of, without)
an- (absence of, without)
crypt- (hidden)
dys- (painful, difficult)
en- (in)
epi- (above)
hyper- (above, excessive)
hypo- (below)
par- (near)
trans- (through, across, beyond)
Combining Forms
andr/o (male)
balan/o (glans penis)
epididym/o (epididymis)
gonad/o (gonad)
orch/o (testis, testicle)
orchi/o (testis, testicle)
orchid/o (testis, testicle)
pen/o (penis)
pen/i (penis)
phall/o (penis)
preputi/o (prepuce, foreskin)
posth/o (prepuce, foreskin)
prostat/o (prostate gland)
scrot/o (scrotum)
semin/i (semen)
sperm/o (sperm, spermatozoon)
spermat/o (sperm, spermatozoon)
test/o (testis, testicle)
testicular/o (testis, testicle)
vas/o (vas deferens, vessel, duct)
vesicul/o (seminal vesicle)
urethr/o (urethra)
Suffixes
-al (pertaining to)
-algia (pain)
-ar (pertaining to)
-atic (pertaining to)
-cision (processing of cutting)
-ectomy (excision or surgical removal)
-ferous (pertaining to)
-genesis ((beginning, development, or production))
-gram (record)
-graphy (process of recording)
-ia (diseased state, abnormal state, condition of, condition)
-ic (pertaining to)
-ile (pertaining to)
-ism (state of, condition)
-itis (inflammation)
-logy (study of)
-lysis (loosening, dissolution, separating)
-oma (tumor, mass)
-ous (pertaining to)
-pathy (disease)
-pexy (surgical fixation, suspension)
-plasia (development, growth)
-plasty (surgical repair)
-rrhea (flow, discharge)
-sis (condition)
-stomy (creation of new opening, process of new opening)
-tion (process of)
-tomy (cut into, incision)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following terms.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
Practice pronouncing and defining these medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
ablation (a-BLĀ-shŏn)
acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) (ă-KWĪRD im-yŭ-nō-dĕ-FISH-ĕn-sē SĬN-drōm)
artificial insemination (art-ĭ-FISH-ăl in-sem-ĭ-NĀ-shŏn)
azoospermia (ā-zō-ŏ-SPĔR-mē-ă)
chlamydia (klă-MID-ē-ă)
circumcision (sĭr-kŭm-SIZH-ŏn)
coitus (KŌ-ĭ-tŭs)
condom (KON-dŏm)
ejaculation (i-jak-yŭ-LĀ-shŏn)
enucleation (ē-nū-klē-Ā-shŭn)
erectile dysfunction (ED) (ĕ-RĔK-tīl dis-FŬNGK-shŏn)
genital herpes (JEN-ĭt-ăl HĔRP-ēz)
gonorrhea (gon-ŏ-RĒ-ă)
human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) (hu-man im-yŭ-nō-dĕ-FISH-ĕn-sē VĪ-rŭs)
human papillomavirus (HPV) (hu-man PAP-ĭ-LŌ-mă-VĪ-rŭs)
hydrocele (HĪ-drŏ-sēl)
hydrocelectomy (hī-drō-sē-LĔK-tō-mē)
infertility (in-fĕr-TIL-ĭt-ē)
metastasis (mĕ-TAS-tă-sĭs)
morcellation (mor-sĕ-LĀ-shŏn)
MRI ultrasound fusion biopsy (FŪ-zhŏn BĪ-op-sē)
orgasm (OR-gazm)
phimosis (fī-MŌ-sĭs)
priapism (PRĪ-ă-pizm)
prostate cancer (PROS-tāt KAN-sĕr)
puberty (PŪ-bĕrt-ē)
robotic surgery (rō-BŎ- tĭk SŬRJ-ĕ-rē)
sexually transmitted disease (STD) (SEKS-ū-ă-lē trăns-MĬT-ed diz-ĒZ)
spermatocele (spĕr-MĂT-ō-sēl)
sterility (stĕ-RIL-ĭt-ē)
sterilization (ster-ĭ-lĭ-ZĀ-shŏn)
syphilis (SIF-ĭ-lĭs)
testicular cancer (tĕs-TĬK-ū-lăr KAN-sĕr)
testicular torsion (tĕs-TĬK-ū-lăr TOR-shŏn)
transurethral (trans-ū-RĒ-thrăl)
transurethral incision of the prostate gland (TUIP)
transurethral resection of the prostate gland (TURP)
transurethral microwave thermotherapy (TUMT)
trichomoniasis (trĭk-ō-mō-NĪ-ă-sĭs)
variocele (VAR-ĭō-sēl)
Practice pronouncing and defining these common abbreviations.
Male Reproductive System Abbreviations
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome)
BPH (benign prostatic hyperplasia, benign prostatic hypertrophy)
Bx (biopsy)
DRE (digital rectal examination)
ED (erectile dysfunction)
GU (genitourinary)
HIV (human immunodeficiency virus)
HoLEP (holmium laser enucleation of the prostate gland)
HPV (human papillomavirus)
HSV-2 (herpes simplex virus 2)
LUTS (lower urinary tract symptoms)
PSA (prostate-specific antigen)
PVP (photoselective vapourization of the prostate gland)
RP (radical prostatectomy)
STD (sexually transmitted disease)
STI (sexually transmitted infection)
TRUS (transrectal ultrasound)
TSE (testicular self-examination)
TUIP (transurethral incision of the prostate gland)
TUMT (transurethral microwave thermotherapy)
TURP (transurethral resection of the prostate gland)
VD (venereal disease)
Reproductive Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) Abbreviations
AB (Antibiotic)
CT (Chlamydia)
GC (Gonorrhea)
HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
HSV (Herpes Simplex Virus)
PID (Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
STD (Sexually Transmitted Diseases)
STI (Sexually Transmitted Infections)
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories.
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Use terms related to the male reproductive system.
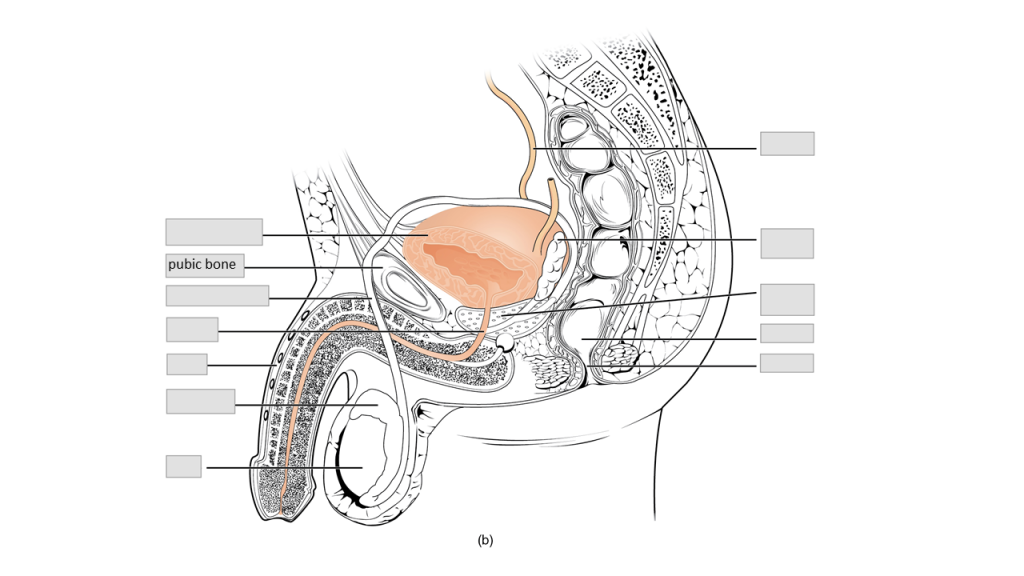
Label the following male reproductive system anatomy.
anus | epididymis | penis | prostate gland | rectum | seminal vesicle | testis | ureter | urethra | urinary bladder | vas deferens
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
by mouth | circumcised | complete | prostatitis | Urethral
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM – MEDICAL REPORT
PATIENT NAME: George SMITH
AGE: 57
SEX: Male
HISTORY (Hx): George Smith is a 57-year-old male who was referred to the urologist for a vasectomy.
FAMILY HISTORY: Has three living children. Occasional condom use for birth control.
PAST HISTORY
- Herpes Simples Virus-2 (HSV-2) diagnosis (Dx) in 2002 and treated sexually transmitted infection
(STI) in 2014. - Transurethral rection of the prostate (TURP) in 2019.
- Current prostate specific antigen (PSA) is 15.6, with a previous result of 4.2.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION/ASSESSMENT: Upon examination, normal male anatomy with ________ penis, normal foreskin and one testicle is descended. Leukorrhea is evident from the tip of the urethral os.
Complains of (c/o) urinary retention, nocturia and dysuria. He has had unprotected sexual intercourse four days ago. Digital rectal exam (DRE) indicated ________ with proctalgia.
DIAGNOSIS (Dx)
- Urethral swab for gonorrhea/chlamydia (GC/CT).
- Serology: PSA, ________ blood count (CBC).
- Urine: Urinalysis, GC/CT, culture and sensitivity (C&S).
- Sonography for the undescended testicle.
MEDICATIONS (Rx)
- Ceftriaxone 250 mg intramuscular immediately (IM STAT)
- Azithromycin 1 g ________ immediately (po STAT)
PRELIMINARY CONCERNS
- Rising PSA.
- ________ discharge.
- Undescended.
FOLLOW UP: Call office in 5 days for test results and follow up appointment in 2 weeks to discuss further booking of vasectomy and potential Bx (biopsy) of prostate.
_______________________
Steve Fosters, MD, Urology
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
The reproductive organs (testes in men and ovaries in women) that produce gametes and reproductive hormones…
- Penis
- Semen
- Gonads
The transformation of spermatids to spermatozoa during spermatogenesis…
- Spermiogenesis
- Ductus deferens
- Prepuce
Glands that secrete a lubricating mucus that cleans and lubricates the urethra prior to and during ejaculation
- Bulbourethral glands
- Scrotum
- Testes
A doughnut-shaped gland at the base of the bladder surrounding the urethra and contributing fluid to semen during ejaculation
- Epididymis
- Prostate gland
- Seminal vesicle
Opening in the abdominal wall that connects the testes to the abdominal cavity…
- Sertoli cells
- Inguinal canal
- Gamete

