3 Integumentary System
Topic: Integumentary System
Text Reference: Chapter 3. Integumentary System
Objectives: Students should be able to…
Identify meanings of key word components of the integumentary system
Prefixes
a- (absence of, meaning)
bi- (two or both)
dia- (through, complete)
dys- (difficult, painful, abnormal, labored)
epi- (upon, on, over)
hyper- (above, excessive)
hypo- (deficient, below, under, incomplete)
intra- (within, in)
meta- (change, beyond, after)
neo- (new)
para- (beside, around, beyond, abnormal)
per- (through)
pro- (before)
sub- (under, below)
trans- (through, across, beyond)
uni- (one)
Combining Forms
aden/o (gland)
adip/o (fat)
albin/o (white)
aut/o (self)
bi/o (life)
coni/o (dust)
cry/o (cold)
crypt/o (hidden)
cutane/o (skin)
cyan/o (blue)
derm/o (skin)
dermat/o (skin)
erythr/o (red)
erythemat/o (redness)
fibr/o (fibrous tissues)
heter/o (other)
hidr/o (sweat)
kerat/o (hard, horny tissue, keratin)
lei/o (smooth)
leuk/o (white)
lip/o, lipid/o (fat)
melan/o (black)
myc/o (fungus)
necr/o (death)
onych/o (nail)
pachy/o (thick)
pil/o (hair)
py/o (pus)
rhytid/o (wrinkles)
sclera/o (hardening)
seb/o (sebum)
staphyl/o (grapelike clusters)
steat/o (fat, sebum)
strept/o (twisted chains)
ungu/o (nail)
xanth/o (yellow)
xer/o (dryness, dry)
Suffixes
-a (no meaning, noun ending)
-al (pertaining to)
-ad (toward)
-coccus (berry-shaped)
-cyte (cell)
-ectomy (excision)
-gen (substance that produces/causes, agent that produces/causes)
-genic (producing, originating, causing)
-ia (condition of, diseased state, abnormal state)
-ic (pertaining to)
-itis (inflammation)
-ior (pertaining to)
-logy (study of)
-logist (specialist who studies and treats)
-malacia (softening)
-megaly (enlarged, enlargement)
-oid (resembling)
-oma (tumor, swelling)
-opsy (view of, process of viewing, viewing)
-orrhea (flow, excessive discharge)
-osis (abnormal condition, increased numbers relating to blood)
-ous (pertaining to)
-pathy (disease)
-phagia (eating, swallowing)
-plasia (development, growth, condition of formation)
-plasm (growth, substance, formation)
-plasty (surgical repair)
-rrhea (flow, discharge)
-sis (state of)
-stasis (stop, controlling, standing)
-tome (instrument used to cut)
Apply the rules of medical language to pronounce, break into word parts, and define the following integumentary system words.
Label each word part by using the following abbreviations:
P = Prefix
WR = Word Root
CV = Combining Vowel
S = Suffix
CF = Combining Form
Example: osteoarthropathy (ä-stē-ō-är-THROP-ă-thē) – disease of bone and joint
WR CV WR CV S
oste / o / arthr / o /pathy
CF CF
biopsy (bx) (BĪ-op-sē)
dermatitis (dĕr-mă-TĪT-ĭs)
dermatoautoplasty (dĕr-mă-tō-AW-tō-plăs-tē)
dermatoconiosis (dĕr-mă-tō-kō-nē-Ō-sĭs)
dermatofibroma (dĕr-mă-tō-fī-BRŌ-mă)
dermatoheteroplasty (dĕr-mă-tō-HĔT-ĕr-ō-plăs-tē)
dermatologist (dĕr-mă-TŎL-ō-jĭst)
dermatology (derm) (dĕr-mă-TŎL-ō-jē)
dermatome (DĔR-mă-tōm)
dermatoplasty (DĔR-măt-ō-plas-tē)
epidermal (ĕp-ĭ-DĔR-mal)
erythroderma (ĕ-rith-rŏ-DĔR-mă)
hidradenitis (hi-dra-ĕn-ĪT-ĭs)
hypodermic (hī-pō-DĔR-mĭk)
intradermal (ID) (in-tră-DĔR-măl)
keratogenic (kĕr-ă-TŎJ-ĕ-nŭk)
keratosis (ker-ă-TŌ-sĭs)
leiodermia (lī-ō-DĔR-mē-ă)
leukoderma (loo-kŏ-DĔR-mă)
necrosis (nĕ-KRŌ-sĭs)
onychocryptosis (ŏn-ĭ-kō-krip-TŌ-sis)
onychomalacia (ŏn-ĭ-kō-mă-LĀ-shă)
onychomycosis (on-i-kō-mī-KŌ-sĭs)
onychophagia (ŏn-ĭ-KŎF-ă-jē)
pachyderma (pak-ē-DĔR-mă)
paronychia (păr-ō-NĬK-ē-ă)
percutaneous (pĕr-kū-TĀ-nē-ŭs)
rhytidectomy (rit-ĭ-DEK-tŏ-mē)
rhytidoplasty (RĬT-ĭ-dō-plăs-tē)
seborrhea (sĕb-or-Ē-ă)
staphylococcus (staph) (staf-ĭ-lō-KOK-ŭs)
streptococcus (strep) (strep-tŏ-KOK-ŭs)
subcutaneous (subcut, Sub-Q) (sŭb-kū-TĀ-nē-ŭs)
subungual (sŭb-ŬNG-gwăl)
transdermal (TD) (trănz-DĔRM-ăl)
ungual (ŬNG-gwăl)
xeroderma (zer-ŏ-DĔR-mă)
xerosis (zĕ-RŌ-sĭs)
Practice pronouncing and defining these integumentary system medical terms that are not easily broken into word parts.
abrasion (ă-BRĀ-zhŏn)
abscess (AB-ses)
acne (AK-nē)
adipocytes (AD-ĭ-pō-sīts)
adipose (AD-ĭ-pōs)
albinism (AL-bĭ-nizm)
apocrine sweat gland (AP-ŏ-krĕn swet gland)
autonomic (ot-ŏ-NOM-ik)
bacteria, bacterium (bak-TĒR-ē, bak-TĒR-ē-ŭm)
basal cell carcinoma (BCC) (BĀ-săl sel kar-sĭn-Ō-ma)
benign (bē-NĪN)
cancer (KAN-sĕr)
cauterize, cauterization (KAW-tĕr-īz)
cellulitis (sel-yŭ-LĪT-ĭs)
contusion (kŏn-TOO-zhŏn)
cyanosis (sī-ă-NŌ-sĭs)
cyst (sist)
debride, debridement (di-BRĒD, di-BRĒD-mĕnt)
dehydration (dē-hī-DRĀ-shŏn)
dendritic cells (den-DRIT-ik)
dermabrasion (DĔRM-ă-brā-zhŏn)
dermis (DĔR-mĭs)
diaphoresis (dī-ă-fŏ-RĒ-sĭs)
eccrine sweat gland (ĔK-rĭn swet gland)
eczema (eg-ZĒ-mă)
edema (ĕ-DĒ-mă)
excise, excision (ĕk-SĪZ, ek-SIZH-ŏn)
fascia (FASH-ē-ă)
frostbite (FROST-bīt)
gangrene (GANG-grēn)
incise, incision (in-SĪZ, in-SIZH-ŏn)
incision and drainage (I&D) (in-SIZH-ŏn & DRĀN-ăj)
infection (in-FEK-shŏn)
jaundice, jaundiced (JON-dĭs, JON-dĭsd)
keloid (KĒ-loyd)
keratin (KER-ăt-ĭn)
keratinocyte (kĕ-RĂT-ĭ-nō-sīt)
laceration (las-ĕ-RĀ-shŏn)
laser surgery (LĀ-zĕr SŬRJ-ĕ-rē)
lesion (lĒ-zhŏn)
leukoplakia (loo-kō-PLĀ-kē-ă)
macule (MAK-ūl)
Meissner corpuscle (MĪS-nĕr KOR-pŭs-ĕl)
melanoma (mel-ă-NŌ-mă)
metastasize (mĕ-TĂS-tă-sīz)
nevus (NĒ-vŭs)
nodule (NOJ-ool)
pallor (PĂL-or)
Pacinian corpuscle (pă-SIN-ē-ăn KOR-pŭs-ĕl)
pallor (PĂL-or)
pathogens (path-Ŏ-jĕns)
phagocytes (făg-ō-SĬTS)
pruritus (proo-RĪT-ŭs)
psoriasis (sŏ-RĪ-ă-sĭs)
pustule (PŬS-tūl)
reticulated (rĕ-TIK-yŭ-lāt-ĕd)
rickets (RIK-ĕts)
scar (skăr)
sebaceous gland (sē-BĀ-shŭs gland)
squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) (SKWĀ-mŭs sel kar-sĭn-Ō-mă)
stratum basale (STRĀ-tŭm BĀS-al)
suture (SOO-chŭr)
sympathetic (sĭm-pă-THĔT-ĭk)
Sympathetic Nervous System (sĭm-pă-THĔT-ĭk NĔR-vŭs SIS-tĕm)
tinea (TIN-ē-ă)
vascularized (VAS-kyŭ-lă-rīzd)
verruca (vĕr-ROO-kă)
virus (VĪ-rŭs)
Practice pronouncing and defining these commonly abbreviated integumentary system terms.
BCC (basal cell carcinoma)
bx (biopsy)
CA-MRSA (community-associated MRSA)
derm (dermatology)
HA-MRSA (healthcare-associated MRSA)
I&D (incision and drainage)
ID (intradermal)
MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus)
SCC (squamous cell carcinoma)
SLE (systemic lupus erythematosus)
staph (staphylococcus)
strep (streptococcus)
subcut, Sub-Q (subcutaneous)
TD (transdermal)
Sort the terms from the word lists above into the following categories.
- Disease and Disorder (terms describing any deviation from normal structure and function)
- Diagnostic (terms related to process of identifying a disease, condition, or injury from its signs and symptoms)
- Therapeutic (terms related to treatment or curing of diseases)
- Anatomic (terms related to body structure)
Use terms related to the integumentary system.
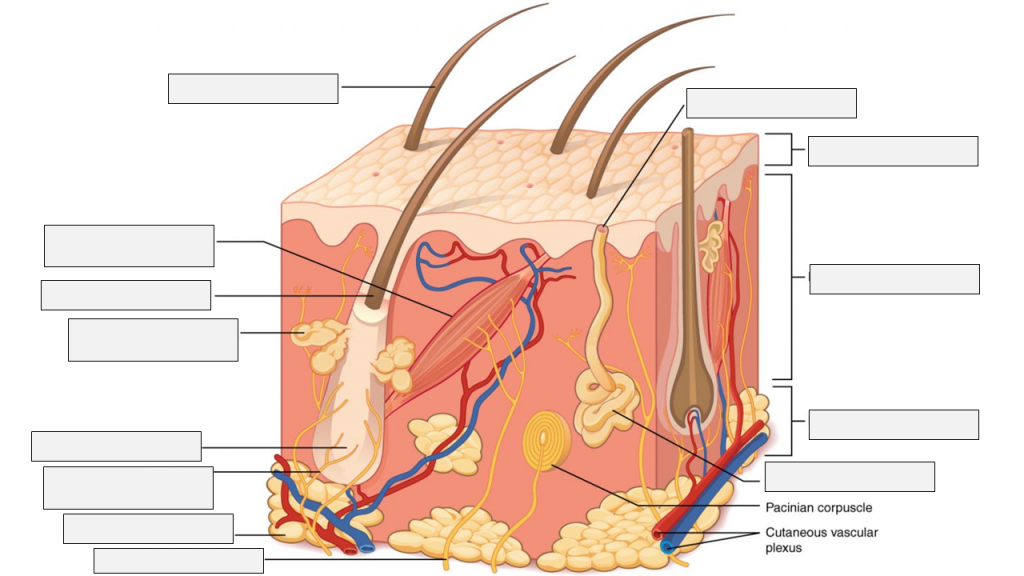
Practice labeling the layers of the skin.
adipose tissue | arrector pili muscle | dermis | eccrine sweat gland | epidermis | hair follicle | hair follicle | hair root | hair shaft | hypodermis | pore of sweat gland | sebaceous/oil gland | sensory nerve fiber
Place the following medical terms in context to complete the scenario below.
benign | lesion | asymmetrical | biopsy | mole | excisional | irregular
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM – CONSULTATION REPORT
PATIENT NAME: Rosemary COOMBS
AGE: 54
Sex: Female
DOB: December 2
DATE OF CONSULTATION: May 29
REQUESTING PHYSICIAN: Trevor Sharpe, MD, Family Medicine
CONSULTING PHYSICIAN: Donna Brown, MD, Dermatology
HISTORY: This 54-year-old white female, went to her family doctor a year ago when she noticed a dark brown spot on her neck. The spot was a six cm, dark brown, flat _________ with smooth borders that appeared _________. Ms. Coombs recently went to Dr. Sharpe for a physical and the was examined, it was suggested that Ms. Coombs see me.
PAST HISTORY: No known history of any skin disorders.
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION: Normal except for the lesion on her chest which has grown to 1.3 cm in diameter and _________ in shape. It is mainly dark brown, with regions of darker black. The borders are _________ in outline. There is some blackened areas that are slightly elevated.
PLAN: I have booked a follow up appointment for next week to do an _________ biopsy. I will then send the specimen for a _________ . Another follow up appointment will be made once I receive the results of the biopsy.
Donna Brown, MD, Dermatology
Practice filling in the blanks with the correct word parts.
Remember combining form vowels are indicated with a line on each side.
al | ectomy | trans | derm | rhytid | cutane | ous | ous | logist | auto | xero | o | phagia | derma | derma | o | sis | dermat | hidr | o | tone | o | aden | kerat | necr | cutane | onycho | plasty | per | genic | dermat | itis | sub
________/________/________/________ refers to the surgical repair of one’s own skin.
Something that generates the production of epidermal tissues might be called ________/________/________.
________/________/________ refers to something in a state of death.
________/________ is a technical name for nail-biting.
________/________/________ means pertaining to through the skin.
________/________/________ injection is given under the skin.
During the winter months many people complain of ________/________ and use extra lotion.
A patch filled with medication,applied to the skin so that medication goes through the skin is referred to as a ________/________/________ patch.
An instrument used to cut the skin for biopsy is referred to as a ________/________.
A specialist who studies and treats disorders and diseases of the skin is referred to as a ________/________/________.
The medical term that means a sweat gland is inflamed is ________/________/________.
The medical term to excise wrinkles or commonly referred to as a facelift is ________/________.
Test your knowledge by answering the questions below.
Cells that manufacture and store the protein keratin
- Keratinocytes
- Vascularized
- Scar
The outer layer of skin, made of closely packed epithelial cells
- Epidermis
- Fascia
- Adipocytes
Specialized cells that produce melanin which is a dark pigment responsible for coloration of skin and hair
- Necrosis
- Melanocytes
- Keloid
Deepest layer of the epidermal
- Stratum basale
- Fascia
- Dermis
Production of cells that can mobilize and establish tumors in other organs of the body
- Pathogens
- Metastasize
- Debridement

