21 Early Theories of Motivation
OpenStax
- What are the basic principles of Frederick Taylor’s concept of scientific management?
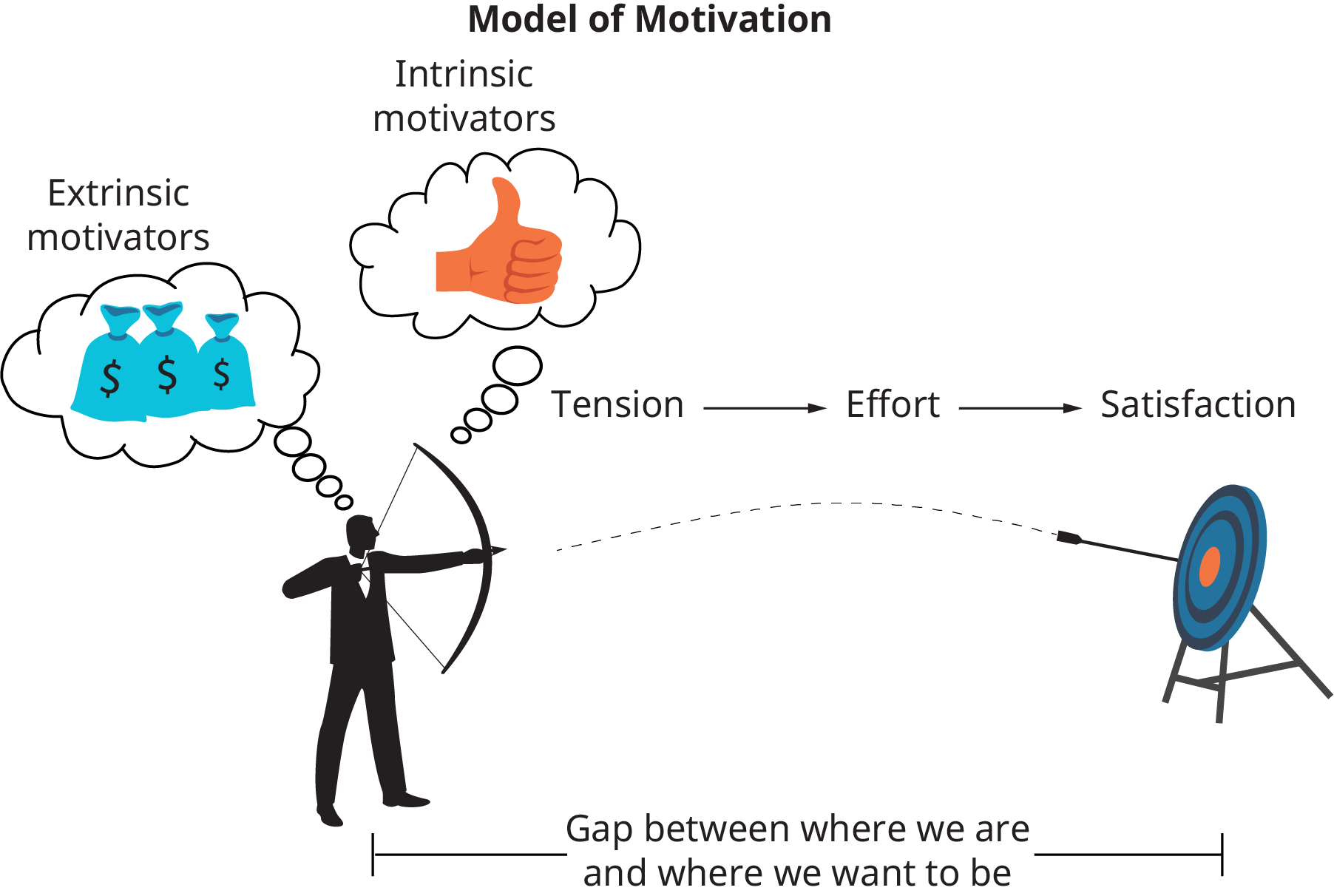
Motivationis the set of forces that prompt a person to release energy in a certain direction. As such, motivation is essentially a need- and want-satisfying process. A needis best defined as the gap between what is and what is required. Similarly, a wantis the gap between what is and what is desired. Unsatisfied needs and wants create a state of tension that pushes (motivates) individuals to practice behavior that will result in the need being met or the want being fulfilled. That is, motivation is what pushes us to move from where we are to where we want to be, because expending that effort will result in some kind of reward.
Rewards can be divided into two basic categories: intrinsic and extrinsic. Intrinsic rewards come from within the individual—things like satisfaction, contentment, sense of accomplishment, confidence, and pride. By contrast, extrinsic rewards come from outside the individual and include things like pay raises, promotions, bonuses, prestigious assignments, and so forth. (Figure)illustrates the motivation process.
Successful managers are able to marshal the forces to motivate employees to achieve organizational goals. And just as there are many types of gaps between where organizations are and where they want to be, there are many motivational theories from which managers can draw to inspire employees to bridge those gaps. In this chapter, we will first examine motivational theories that grew out of the industrial revolution and early ideas of organizational psychology. Then we will examine needs-based theories and more contemporary ideas about employee motivation like equity, expectancy, goals, and reinforcement theories. Finally, we will show you how managers are applying these theories in real-world situations.
How can managers and organizations promote enthusiastic job performance, high productivity, and job satisfaction? Many studies of human behavior in organizations have contributed to our current understanding of these issues. A look at the evolution of management theory and research shows how managers have arrived at the practices used today to manage human behavior in the workplace. A sampling of the most influential of these theorists and research studies are discussed in this section.
Frederick Taylor’s Scientific Management
One of the most influential figures of the classical eraof management, which lasted from about 1900 to the mid-1930s, was Frederick W. Taylor, a mechanical engineer sometimes called the “father of scientific management.” Taylor’s approach to improved performance was based on economic incentives and the premise that there is “one best way” to perform any job. As a manager at the Midvale and Bethlehem Steelcompanies in Philadelphia in the early 1900s, Taylorwas frustrated at the inefficiency of the laborers working in the mills.
Convinced that productivity could be improved, Taylorstudied the individual jobs in the mill and redesigned the equipment and the methods used by workers. Taylor timed each job with a stopwatch and broke down every task into separate movements. He then prepared an instruction sheet telling exactly how each job should be done, how much time it should take, and what motions and tools should be used. Taylor’s ideas led to dramatic increases in productivity in the steel mills and resulted in the development of four basic principles of scientific management:
- Develop a scientific approach for each element of a person’s job.
- Scientifically select, train, teach, and develop workers.
- Encourage cooperation between workers and managers so that each job can be accomplished in a standard, scientifically determined way.
- Divide work and responsibility between management and workers according to who is better suited to each task.
Taylor published his ideas in The Principles of Scientific Management.His pioneering work vastly increased production efficiency and contributed to the specialization of labor and the assembly-line method of production. Taylor’s approach is still being used nearly a century later in companies such as UPS, where industrial engineers maximize efficiency by carefully studying every step of the delivery process looking for the quickest possible way to deliver packages to customers. Though Taylor’s work was a giant step forward in the evolution of management, it had a fundamental flaw in that it assumed that all people are primarily motivated by economic means. Taylor’s successors in the study of management found that motivation is much more complex than he envisioned.
- How did Frederic Taylor’s studies contribute to the early understanding of human motivation?
- How are Taylor’s insights still seen in today’s management practices?
Summary of Learning Outcomes
- What are the basic principles of Frederick Taylor’s concept of scientific management?
Scientific management is based on the belief that employees are motivated by economic incentives and that there is “one best way” to perform any job. The four basic principles of scientific management developed by Taylor are as follows:
- Develop a scientific approach for each element of a person’s job.
- Scientifically select, train, teach, and develop workers.
- Encourage cooperation between workers and managers so that each job can be accomplished in a standard, scientifically determined way.
- Divide work and responsibility between management and workers according to who is better suited to each task.
Glossary
- motivation
- Something that prompts a person to release his or her energy in a certain direction.
- need
- The gap between what is and what is required.
- scientific management
- A system of management developed by Frederick W. Taylor and based on four principles: developing a scientific approach for each element of a job, scientifically selecting and training workers, encouraging cooperation between workers and managers, and dividing work and responsibility between management and workers according to who can better perform a particular task.
- want
- The gap between what is and what is desired.

