137 Chapter 10 Monopoly and Antitrust Policy Answer Key
Chapter 10 Monopoly and Antitrust Policy Answer Key
1. Yes, it is true. The HHI example is easy enough: since the market shares of all firms are included in the HHI calculation, a merger between two of the firms will change the HHI. For the four-firm concentration ratio, it is quite possible that a merger between, say, the fifth and sixth largest firms in the market could create a new firm that is then ranked in the top four in the market. In this case, a merger of two firms, neither in the top four, would still change the four-firm concentration ratio.
2. No, it is not true. The HHI includes the market shares of all firms in its calculation, but the squaring of the market shares has the effect of making the impact of the largest firms relatively bigger than in the 4-firm or 8-firm ratio.
3. The bus companies wanted the broader market definition (i.e., the second definition). If the narrow definition had been used, the combined bus companies would have had a near-monopoly on the market for intercity bus service. But they had only a sliver of the market for intercity transportation when everything else was included. The merger was allowed.
4. The common expectation is that the definition of markets will become broader because of greater competition from faraway places. However, this broadening doesn’t necessarily mean that antitrust authorities can relax. There is also a fear that companies with a local or national monopoly may use the new opportunities to extend their reach across national borders, and that it will be difficult for national authorities to respond.
5. Because outright collusion to raise profits is illegal and because existing regulations include gray areas which firms may be able to exploit.
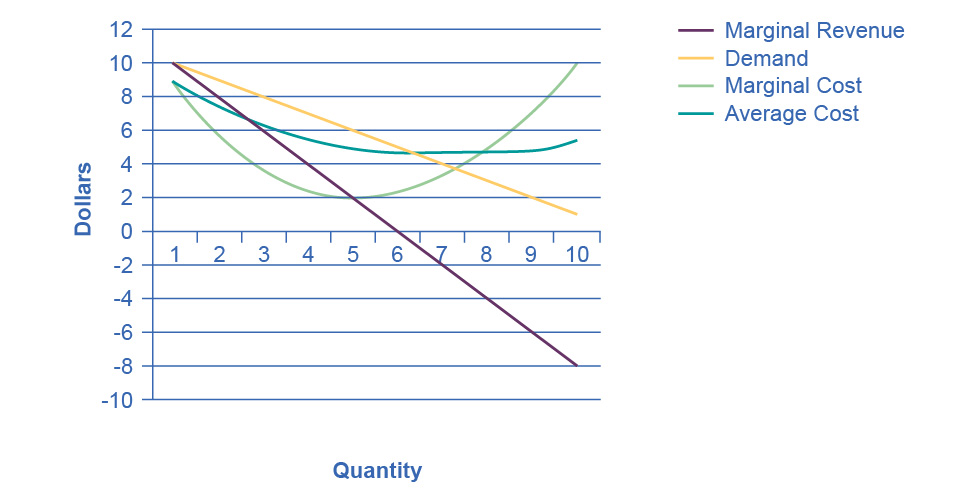
6. Yes, all curves have normal shapes.
7. Yes it is a natural monopoly because average costs decline over the range that satisfies the market demand. For example, at the point where the demand curve and the average cost curve meet, there are economies of scale.
8. Improvements in technology that allowed phone calls to be made via microwave transmission, communications satellites, and other wireless technologies.
9. More consumer choice. Cheaper phone calls, especially long distance. Better-quality phone service in many cases. Cheaper, faster, and better-quality data transmission. Spin-off technologies like free Internet-based calling and video calling.
10. More choice can sometimes make for difficult decisions—not knowing if you got the best plan for your situation, for example. Some phone service providers are less reliable than AT&T used to be.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/principles-economics-3e