Forms of Brand Development, Brand Loyalty, and Brand Metrics
Learning Objectives
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Identify branding strategies.
- Describe degrees of brand loyalty.
Brand Development
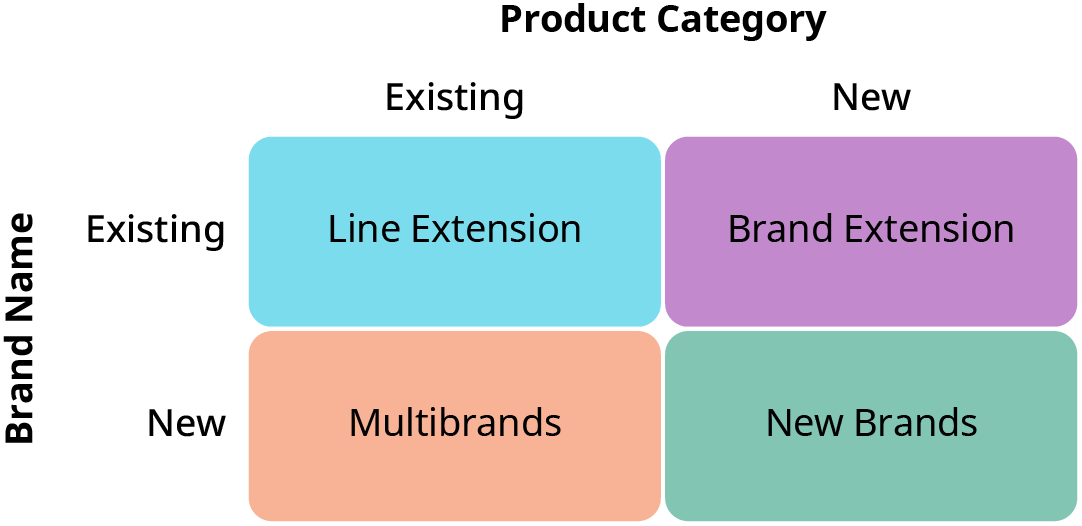
New products can be added to a brand at any time. There are a few ways to add products that are classified on two measures: new/existing brand name and new/existing product category (see Figure 9.8).
Figure 9.8 Brand Development Matrix (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license)
Line extensions create new opportunities for an existing product and brand to serve customers. For example, the Oreo brand adds flavors to its product line for holidays. These line extensions provide the existing brand with an extension of its current product. As a result, a line extension may sell more products to already-aware and interested customers without many risks. However, sometimes brands may overextend their product lines and products may be too similar, failing to increase sales.
Brand extensions leverage the brand name to new product categories. For example, Starbucks developed a line of bottled coffees under its corporate brand name. A brand extension uses awareness and equity in the brand to gain instant recognition and affinity for the new product, which may increase sales rapidly. However, if the new product is inferior to the brand’s known quality, the entire brand portfolio may be at risk.
Multibrands are new brand names within a company’s existing product category. For example, Nabisco manufactures various cookies within a product line but is marketed with different brand names. In this case, Chips Ahoy, Oreo, and Teddy Grahams all have brand equity on their own and do not need the benefit of the Nabisco brand. Each of these brands has a significant market share, so there is a benefit to retaining a multibranding approach. However, a multibranding approach does not work when the products have a small market share or fail to gain favorable retail shelf space to encourage sales.
New brands are an entirely different entity from the parent company. A new brand strategy can be effective if the new product or service is markedly different from the existing offering and benefits from its own branding. For example, the Starbucks brand owns Ethos Water. Ethos is in a beverage category other than Starbucks’s primary offering and retains its name. A new brand strategy works well when the new brand is distinct from the parent brand and has a defined target market and positioning; however, a marketing strategy for a new brand can be expensive to maintain over time.
Brand Loyalty Levels
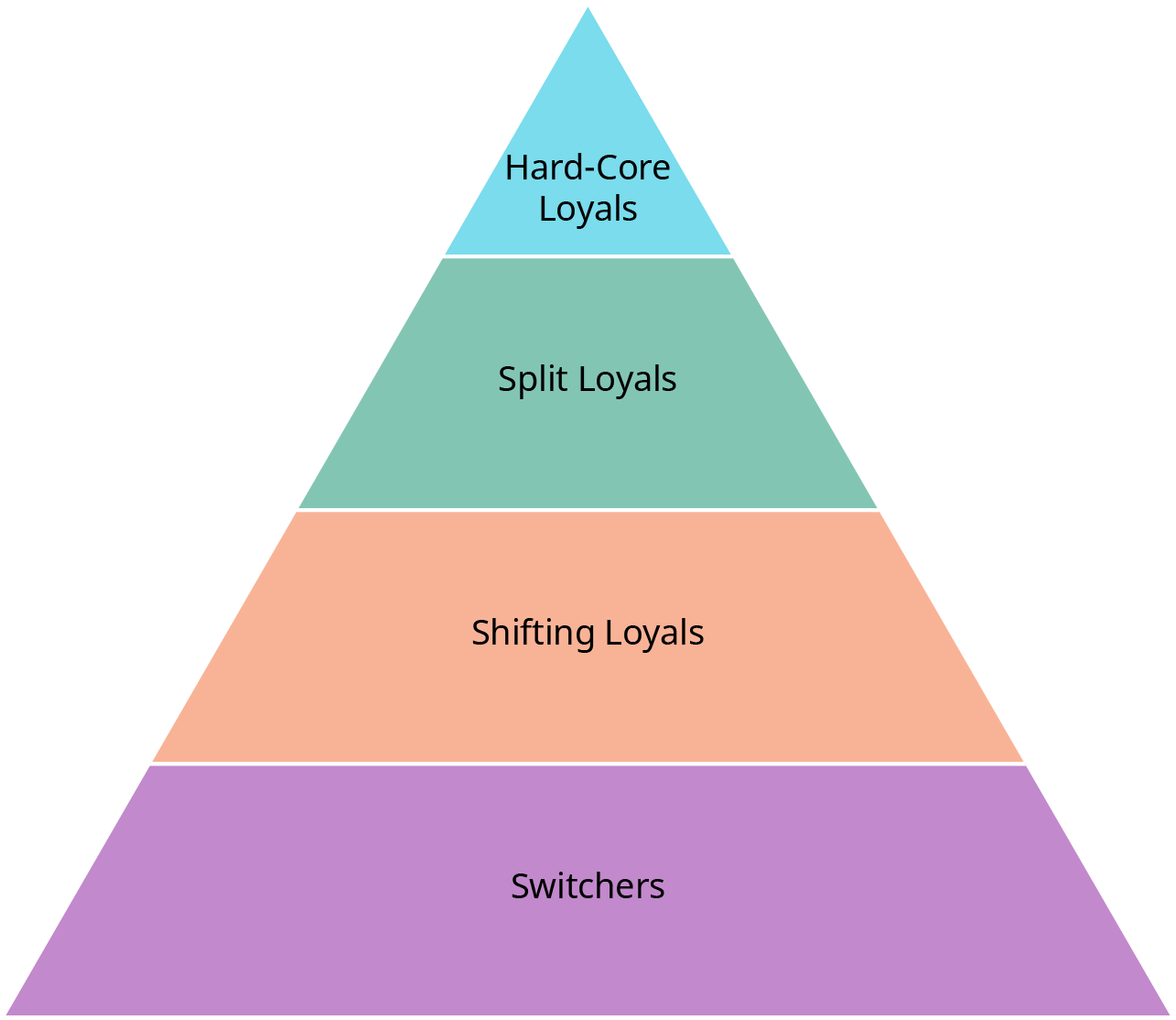
As you can see, brands spend time and resources to gain loyal customers. Loyal customers are the holy grail of marketing because they will purchase your brand and advocate for the brand to others. Loyal customers become instant word of mouth, spreading the positive attributes of a brand. However, not all customers are intensely loyal to one brand. Instead, customers fit into one of four loyalty categories (see Figure 9.9).
Figure 9.9 Loyalty Categories (attribution: Copyright Rice University, OpenStax, under CC BY 4.0 license)
Switchers are customers who continually change their purchasing behaviors. Switchers may be motivated by price, convenience, or innovation. Therefore, it is essential to develop a product or service that meets the switching consumers’ needs to retain them as customers. For example, a switcher might purchase the lowest-price laundry detergent each time they are at the store.
Shifting loyals are customers who are loyal to one product or service for a time, then turn their loyalty to a different product or service for the second period. Brands can expect that shifting loyal customers will move back and forth between products and services. For example, a shifting loyal might purchase a Toyota followed by a Honda, then turn their loyalty back to Toyota for a third purchase.
Split loyals are customers who have a consideration set of two to three products or services in the category. The split loyal is willing to buy this select set of brands on any occasion without hard-core loyalty to any in the group. However, brands can convert split loyals into hard-core loyals with product/service consistency, loyalty programs, and marketing efforts. For example, customers may have loyalty to Gap, Banana Republic, and J.Crew for workwear.
Hard-core loyals are the customers that every brand wants. They are tried-and-true customers who will generally only purchase one brand in a category. For example, when purchasing from a catalog, they tend to make a purchase with less concern about price. In addition, hard-core loyals often tell friends and family about their purchases, extending word-of-mouth marketing for the brand. Brands need to retain hard-core loyal customers. For example, Dunkin’ knows that loyalty is essential to its business, so it rewards its loyal customers with free food and coffee through its DD Perks program.