19 The Role of Management
Learning Objectives
- What is the role of management?
Management is the process of guiding the development, maintenance, and allocation of resources to attain organizational goals. Managers are the people in the organization responsible for developing and carrying out this management process. Management is dynamic by nature and evolves to meet needs and constraints in the organization’s internal and external environments. In a global marketplace where the rate of change is rapidly increasing, flexibility and adaptability are crucial to the managerial process. This process is based in four key functional areas of the organization: planning, organizing, leading, and controlling. Although these activities are discussed separately in the chapter, they actually form a tightly integrated cycle of thoughts and actions.
From this perspective, the managerial process can be described as (1) anticipating potential problems or opportunities and designing plans to deal with them, (2) coordinating and allocating the resources needed to implement plans, (3) guiding personnel through the implementation process, and (4) reviewing results and making any necessary changes. This last stage provides information to be used in ongoing planning efforts, and thus the cycle starts over again. The four functions are highly interdependent, with managers often performing more than one of them at a time and each of them many times over the course of a normal workday.

The four management functions can help managers increase organizational efficiency and effectiveness. Efficiency is using the least possible amount of resources to get work done, whereas effectiveness is the ability to produce a desired result. Managers need to be both efficient and effective in order to achieve organizational goals. For example in 2016, Delta, one of the most efficient network U.S. airlines, operated at revenue of 12.15 cents per seat-mile, which is the revenue the company makes on one seat (occupied or not) the distance of one mile. No other airline came close to operating this efficiently except Southwest, which flew seats that produced 12.51 cents a mile, the best performance of all U.S. airlines.1 There are many ways that airlines can manage to produce higher revenue per seat-mile. For instance, they can raise ticket prices, fill more of their seats, operate more efficient aircraft that utilize less fuel, or negotiate favorable salaries with their employees. While efficiency and effectiveness are sometimes lauded by investors, airlines also need to account for customer satisfaction, which can mean extra costs.2
To meet the demands of rapid growth, Skechers hired a new chief financial officer, John Vandemore, which allowed their existing CFO (David Weinberg) to concentrate on international expansion. Skechers CEO Robert Greenberg commented: “As international now represents more than 50 percent of our total business, we must continue to ramp up operations and infrastructure to meet the demand. David (Weinberg) understands how to do it the right way at the right speed to maintain our forward momentum. With John (Vandemore) handling CFO responsibilities, David will now have the bandwidth to travel and find opportunities to maximize our efficiencies around the globe.”3
What Do Managers Do?
The Management Process
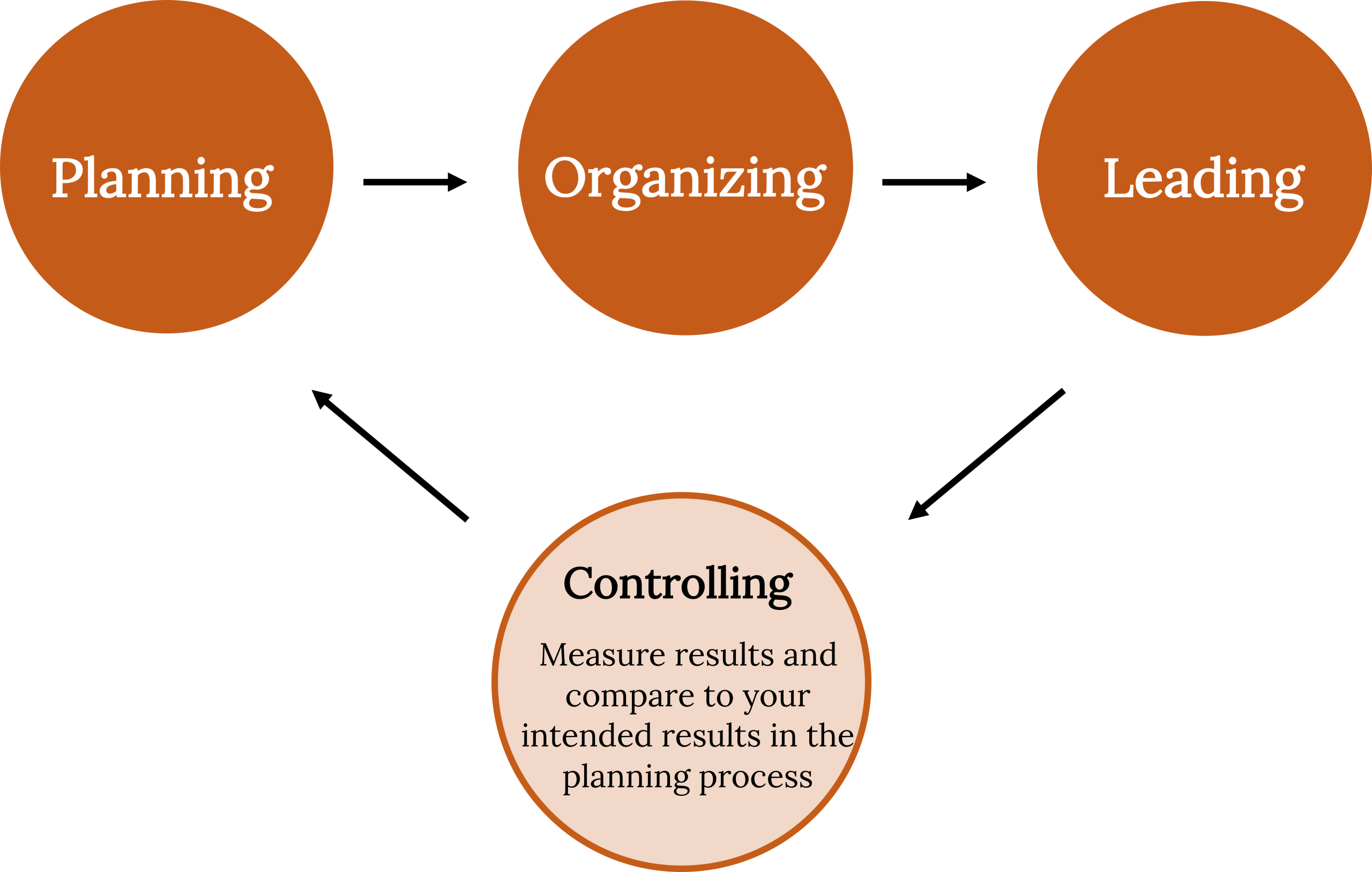
The effective performance of your business will require solid management: the process of planning, organizing, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific goals. A plan enables you to take your business concept beyond the idea stage. It does not, however, get the work done. For that to happen, you have to organize things effectively. You’ll have to put people and other resources in place to make things happen. And because your note-taking venture is supposed to be better off with you in charge, you need to be a leader who can motivate your people to do well. Finally, to know whether things are in fact going well, you’ll have to control your operations—that is, measure the results and compare them with the results that you laid out in your plan. Figure 8.2 summarizes the interrelationship between planning and the other functions that managers perform.
|
What Managers Do and Why |
|||||
|
Good management consists of these four activities: |
|
Which results in |
|
And leads to |
|
|
Planning Set objectives and state mission Examine alternatives Determine needed resources Create strategies to reach objectives |
Leading Lead and motivate employees to accomplish organizational goals Communicate with employees Resolve conflicts Manage change |
Leads to… Organizational efficiency and effectiveness |
Leads to… Achievement of organizational |
||
|
Organizing Design jobs and specify tasks Create organizational structure Staff positions Coordinate work activities Set policies and procedures Allocate resources |
Controlling Measure performance Compare performance to standards Take necessary action to improve performance |
||||
Table 6.1
Roselinde Torres is an extremely accomplished leadership expert, and her TED Talk shares her insights on what it takes to be a great leader. If you have not seen TED Talks before, you will likely see a great many more before you graduate.
What makes a good leader?
Concept Check
- Define the term management.
- What are the four key functions of managers?
- What is the difference between efficiency and effectiveness?
Media Attributions
- 6.2

