Exercise Set B
Exercise Set B
EB 1. Match the correct term with its definition.
|
A. Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) |
i. used by the FASB, which is a set of concepts that guide financial reporting |
|
B. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) |
ii. independent, nonprofit organization that sets financial accounting and reporting standards for both public- and private-sector businesses that use generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) here in the United States |
|
C. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) |
iii. standards, procedures, and principles companies must follow when preparing their financial statements |
|
D. conceptual framework |
iv. assumes a business will continue to operate in the foreseeable future |
|
E. going concern assumption |
v. independent federal agency protecting the interests of investors, regulating stock markets, and ensuring companies adhere to GAAP requirements |
|
F. time period assumption |
vi. companies can present useful information in shorter time periods such as years, quarters, or months |
EB 2. Consider the following accounts and determine if the account is an asset (A), a liability (L), or equity (E).
- Accounts Receivable
- Sales Revenue
- Land
- Unearned Revenue
EB 3. Provide the missing amounts of the accounting equation for each of the following companies.
EB 4. From the following list, identify which items are considered original sources:
- accounts receivable
- receipt from post office for post office box
- purchase order
- general ledger
- adjusted trial balance
- statement of retained earnings
- electric bill
- packing slip
- company expense account
- statement of cash flows
EB 5. Indicate what impact the following transactions would have on the accounting equation, Assets = Liabilities + Equity.
|
|
Impact 1 |
Impact 2 |
|
Paid this month’s utility bill |
|
|
|
Purchased supplies for cash |
|
|
|
Received cash for services performed |
|
|
|
Collected cash from customer accounts receivable |
|
|
|
Paid creditors on account |
|
|
Table 3.9
EB 6. For the following accounts indicate whether the normal balance is a debit or a credit.
- Unearned Revenue
- Interest Expense
- Rent Expense
- Rent Revenue
- Accounts Payable
- Cash
- Supplies
- Accounts Payable
- Equipment
- Utilities Expense
EB 7. Which two accounts are affected by each of the following transactions?
|
|
Account 1 |
Account 2 |
|
Received cash from issuance of common stock |
|
|
|
Purchased land by issuing a note payable |
|
|
|
Paid balance on account for last month’s inventory purchases |
|
|
|
Received cash from customers for this month’s sales |
|
|
|
Sold merchandise to customers on account |
|
|
Table 3.10
EB 8. Identify the normal balance for each of the following accounts. Choose Dr for Debit; Cr for Credit.
|
|
Normal balance |
|
Insurance Expense |
|
|
Accounts Receivable |
|
|
Office Supplies |
|
|
Sales Revenue |
|
|
Common Stock |
|
|
Notes Payable |
|
Table 3.11
EB 9. Identify whether each of the following transactions would be recorded with a debit (Dr) or credit (Cr) entry.
|
|
Debit or credit? |
|
Cash decrease |
|
|
Supplies increase |
|
|
Accounts Payable decrease |
|
|
Common Stock increase |
|
|
Accounts Payable increase |
|
|
Notes Payable increase |
|
Table 3.12
EB 10. Identify whether each of the following transactions would be recorded with a debit (Dr) or credit (Cr) entry.
|
|
Debit or credit? |
|
Equipment increase |
|
|
Dividends Paid increase |
|
|
Repairs Expense increase |
|
|
Service revenue increase |
|
|
Miscellaneous Expense increase |
|
|
Bonds Payable increase |
|
Table 3.13
EB 11. Identify whether ongoing transactions posted to the following accounts would normally have only debit entries (Dr), only credit entries (Cr), or both debit and credit entries (both).
|
|
Type of entry |
|
Notes Payable |
|
|
Accounts Receivable |
|
|
Utilities Expense |
|
|
Sales Revenue |
|
|
Insurance Expense |
|
|
Dividends |
|
Table 3.14
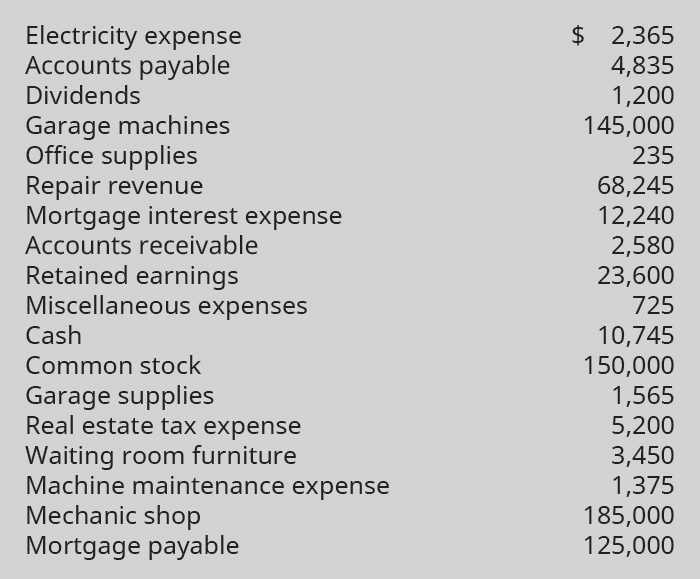
EB 12. West End Inc., an auto mechanic shop, has the following account balances, given in no certain order, for the quarter ended March 31, 2019. Based on the information provided, prepare West End’s annual financial statements (omit the Statement of Cash Flows).
Prepare West End’s annual financial statements. (Omit the Statement of Cash Flows.)
EB 13. State whether the balance in each of the following accounts increases with a debit or a credit.
- Office Supplies
- Retained Earnings
- Salaries Expense
- Accounts Receivable
- Service Revenue
EB 14. Journalize each of the following transactions or state no entry required and explain why. Be sure to follow proper journal writing rules.
- A company is started with an investment of a machine worth $40,000. Common stock is received in exchange.
- Office furniture is ordered. The furniture worth $7,850 will be delivered in one week. The payment will be due forty-five days after delivery.
- An advertisement was run in the newspaper at a total cost of $250. Cash was paid when the order was placed.
- The office furniture is delivered.
- Services are performed for a client. The client was billed for $535.
EB 15. Discuss how each of the following transactions will affect assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity, and prove the company’s accounts will still be in balance.
- A company purchased $450 worth of office supplies on credit.
- The company parking lot was plowed after a blizzard. A check for $75 was given to the plow truck operator.
- $250 was paid on account.
- A customer paid $350 on account.
- Provided services for a customer, $500. The customer asked to be billed.
EB 16. For each of the following items, indicate whether a debit or a credit applies.
- increase in retained earnings
- decrease in prepaid rent
- increase in dividends
- decrease in salaries payable
- increase in accounts receivable
- decrease in common stock
- decrease in prepaid insurance
- decrease in advertising expense
- decrease in unearned service fees
- increase in office equipment
EB 17. Indicate whether each of the following accounts has a normal debit or credit balance.
- prepaid landscaping expense
- common stock
- delivery vans
- maintenance expense
- retained earnings
- office supplies
- revenue earned
- accounts payable
- unearned painting revenue
- interest payable
EB 18. Krespy Corp. has a cash balance of $7,500 before the following transactions occur:
- received customer payments of $965
- supplies purchased on account $435
- services worth $850 performed, 25% is paid in cash the rest will be billed
- corporation pays $275 for an ad in the newspaper
- bill is received for electricity used $235.
- dividends of $2,500 are distributed
What is the balance in cash after these transactions are journalized and posted?
EB 19. A business has the following transactions:
- The business is started by receiving cash from an investor in exchange for common stock $10,000.
- Rent of $1,250 is paid for the first month.
- Office supplies are purchased for $375.
- Services worth $3,450 are performed. Cash is received for half.
- Customers pay $1,250 for services to be performed next month.
- $6,000 is paid for a one year insurance policy.
- We receive 25% of the money owed by customers in “D”.
- A customer has placed an order for $475 of services to be done this coming week.
How much total revenue does the company have?
EB 20. Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions.
- November 19, purchased merchandise inventory, on account, $12,000
- November 29, paid creditor for part of November 19 purchase, $10,000
EB 21. Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions:
- December 1, collected balance due from customer account, $5,500
- December 12, paid creditors for supplies purchased last month, $4,200
- December 31, paid cash dividend to stockholders, $1,000
EB 22. Prepare journal entries to record the following transactions:
- October 9, issued common stock in exchange for building, $40,000
- October 12, purchased supplies on account, $3,600
- October 24, paid cash dividend to stockholders, $2,500
EB 23. Post the following August transactions to T-accounts for Accounts Payable and Supplies, indicating the ending balance (assume no beginning balances in these accounts):
- purchased supplies on account, $600
- paid vendors for supplies delivered earlier in month, $500
- purchased supplies for cash, $450
EB 24. Post the following July transactions to T-accounts for Accounts Receivable and Cash, indicating the ending balance (assume no beginning balances in these accounts):
- sold products to customers for cash, $8,500
- sold products to customers on account, $2,900
- collected cash from customer accounts, $1,600
EB 25. Prepare an unadjusted trial balance, in correct format, from the alphabetized account information as follows. Assume all accounts have normal balances.
A free copy of this content can be found at: https://openstax.org/books/principles-financial-accounting